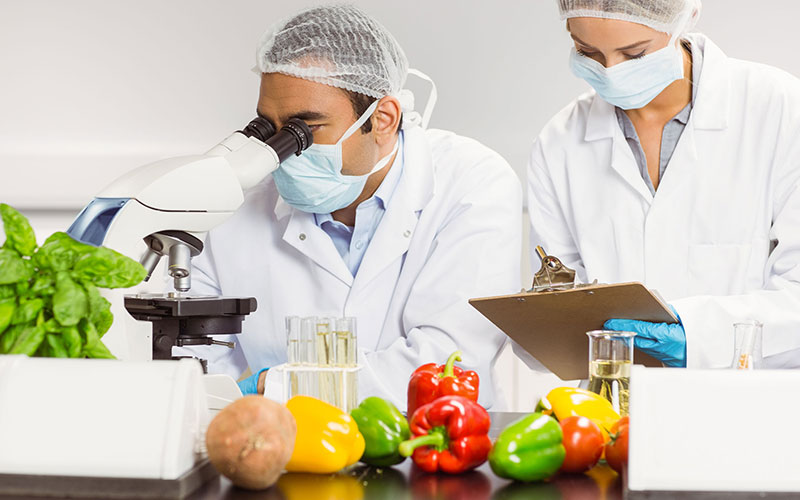
In this article, we will look for the answer to the question What are the Food Safety System Applications? In our previous article, we looked for an answer to the question How to Establish a Food Safety System?
As it is known, if we want to implement a successful system in food safety, it is necessary to support this system with certain applications. We mentioned these applications in our previous article. Now let’s examine these applications in more detail.
Good Agricultural Practices (GAP, EUREPGAP- GLOBALGAP)
GLOBALGAP, or EUREPGRAP, which is a protocol of Good Agriculture Practice (GAP), is an initiative established and implemented in 1997 by the leading European supermarkets to investigate whether the products they offer for sale are harmful to human health.
It is now a worldwide valid standard. Approximately 70-80 of the large-scale retailers and producers in Europe are currently members or registered with GLOBALGAP.
Why GLOBALGAP?
In short, we can list the objectives of GLOBALGAP as follows.
- Reducing risks related to food safety and the environment, the health of consumers and agricultural workers
- minimizing risks
- Taking preventive measures in agricultural practices to prevent faulty products from reaching the buyer prevention of
- Easier compliance with agricultural legal regulations
- Integration of quality studies applied in agricultural enterprises
- Establishing a production approach that takes responsibility for the environment
In line with these objectives;
- For consumers, it reduces food safety and public health concerns. Provides traceability regarding the point of arrival of food.
- For retailers, it reduces the problems they carry regarding consumer health and product safety. It brings about changes in consumers’ purchasing behavior that can be beneficial. Eliminates the complexity of legal regulations.
- For producers, it increases competitiveness and makes competition fairer. Improves product quality and thus reduces production costs in the long term.
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
This standard of practice, GMP, which guarantees the safety and nutritional accuracy of foods, was first proposed for food products by the US FDA in 1967.
Good Manufacturing Practice, which stands for Good Manufacturing Practice, is a prerequisite program that must be applied continuously for many processes such as raw materials, production, product development, packaging, and storage to improve the quality of food products. In short, GMP is a set of business and external measures used to prevent or minimize the possibility of contamination from internal and external sources in the product.
GHP (Good Hygiene Practices)
Good Hygiene Practice, also known as GHP, is concerned with hygienic requirements. Food hygiene is a practice that aims to manage processes such as hygienic designs in production facilities and the configuration of these designs, the placement of tools and equipment according to sanitary design principles, and personnel hygiene.
GLP (Good Laboratory Practice)
GLP, also known as Good Laboratory Practice, stands for Good Laboratory Practice. In short, GLP is one of the complementary elements of quality assurance systems. It is also known as an application of improvement efforts about the laboratory environment and its functioning.
GVP (Good Veterinary Practices)
GVP, which translates into Turkish as Good Veterinary Practice, follows all processes of animal food. For example, it is a standard that ensures that food safety is taken under control in all processes starting from raw materials to the consumer’s table. The system includes topics such as zootechnics, breeding, animal health, animal health in the production process, and hygiene in production, operation, and distribution.
GDP (Good Distribution Practices)
GDP, which is translated into Turkish as good distribution practices, is known as Good Distribution Practice in English. In short, it aims to protect the safety of both animal and vegetable raw materials and semi-finished and finished products obtained as a result of the processing of these raw materials in the distribution processes until the consumption stage. For example, parameters such as the vehicle, temperature, and humidity to be used in the distribution process according to the characteristics of the product should be defined in advance, and the relevant procedures and instructions should be kept in documents.
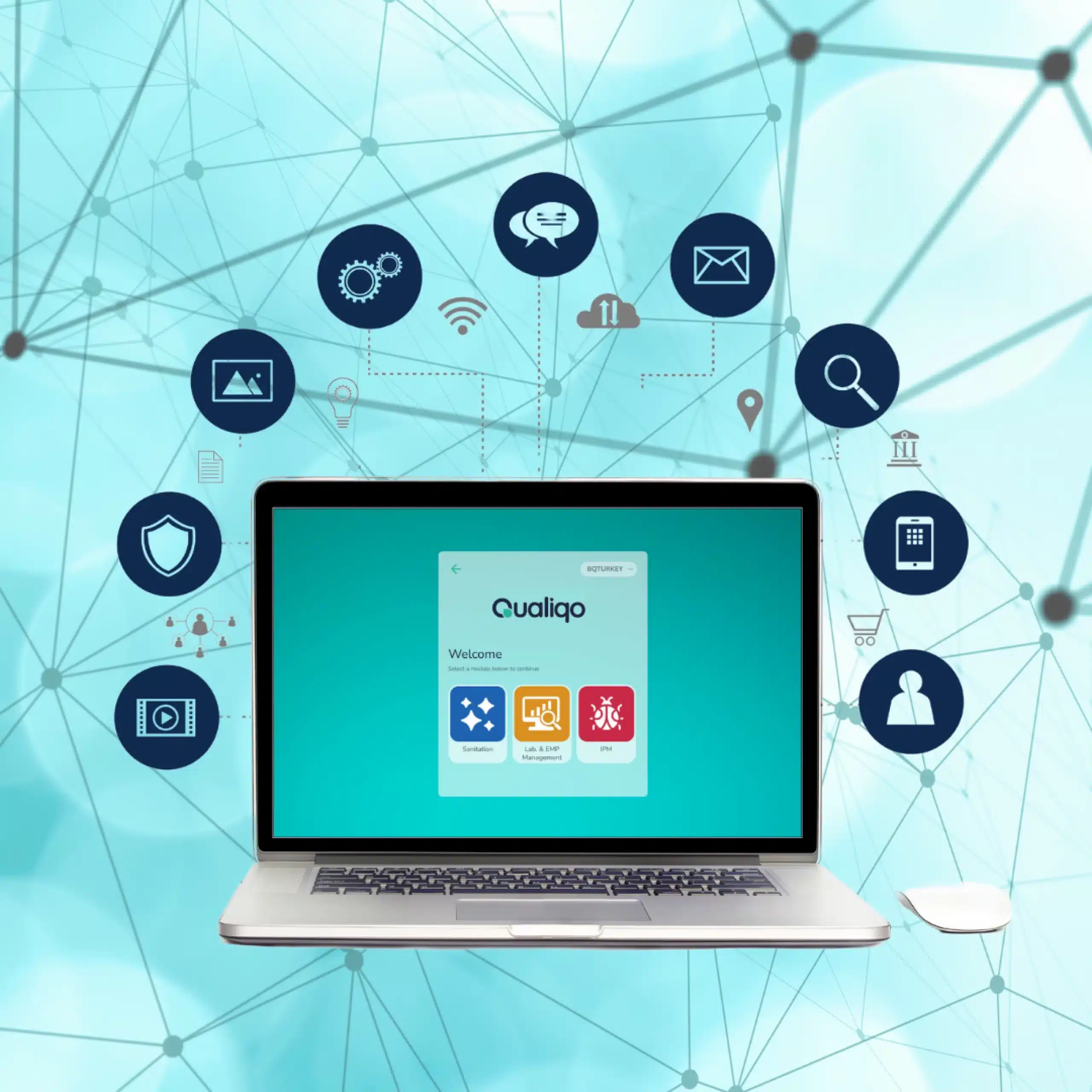
With Qualiqo, which will take you to a paperless environment in many food safety system applications, you can store your instructions in a way that can be accessed from any point.
SSOP (Standard Sanitation Operating Procedures)
SSOP (Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures) are written procedures for defining hygiene conditions for the realization of sanitation conditions in food enterprises and the production of healthy and safe products.
For this purpose, special “hygiene control” programs should be created by authorized persons and hygiene controls should be recorded.
To prevent any contamination of food products by cleaning agents and disinfectants;
All “food contact surface areas” in the facility, including the floor, ducts related to the applied process, walls, and all kinds of tools, machinery and equipment in contact with foodstuffs, should be thoroughly cleaned regularly and kept under microbiological control to protect the food against contamination.
You can contact us to get information about Qualiqo, where you can digitally record such processes.
In this article, we tried to provide you with information about Food Safety System Applications.